PepsiCo is a global powerhouse in the food and beverage industry, known for its iconic products and far-reaching influence. With a diverse product range spanning snacks, beverages, and nutrition, PepsiCo has established itself as a leader competing fiercely with other giants like Coca-Cola and Nestlé. Understanding the company’s internal strengths and weaknesses, along with external opportunities and threats, is crucial for maintaining its market dominance and planning future growth. This is where a thorough SWOT analysis of PepsiCo becomes invaluable.
Conducting a PepsiCo SWOT Analysis helps break down the core factors shaping its business environment. This analysis allows the company and stakeholders to make informed decisions, leverage competitive advantages, address challenges, and seize emerging opportunities. In today’s fast-evolving consumer landscape, such insights are critical for PepsiCo to stay ahead and adapt to shifting trends.
Company Snapshot
To appreciate the nuances in PepsiCo’s SWOT, a brief overview of the company’s background is essential:
- Founded: 1898 by Caleb Bradham as “Brad’s Drink,” later renamed Pepsi-Cola.
- Headquarters: Harrison, New York, USA.
- CEO: Ramon Laguarta (since 2018), credited with steering PepsiCo towards innovation and sustainability.
- Global Presence: PepsiCo operates in over 200 countries worldwide.
- Revenue (2023): Approximately $91.4 billion.
- Employees: Roughly 318,000 across various divisions globally.
This vast footprint reflects PepsiCo’s extensive influence and the challenges it faces in maintaining its brand relevance and operational efficiency on a global scale.
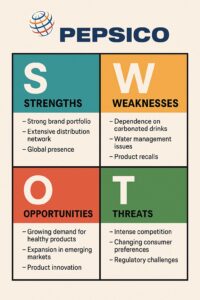
Strengths
Brand Recognition
One of PepsiCo’s most powerful assets is its strong brand recognition. Pepsi, Lay’s, Gatorade, Tropicana, Quaker Oats, and Doritos are just a few examples of brands that have become household names globally. This brand loyalty translates to consumer trust and repeat purchases.
For example, during the FIFA World Cup and the Olympics, PepsiCo’s strategic sponsorships help amplify brand visibility and consumer engagement worldwide. These events not only showcase Pepsi’s refreshing beverages but also associate the brand with excitement, sportsmanship, and global unity.
Diversified Portfolio
PepsiCo’s product portfolio is highly diversified, spanning beverages, salty snacks, cereals, and nutrition products. This diversification reduces dependency on any single product category and allows the company to cater to various consumer preferences. For instance, while soda sales have faced challenges, PepsiCo’s snack segment continues to grow robustly, balancing overall revenue streams.
This strategy has been crucial, especially as consumer tastes evolve. In recent years, PepsiCo has expanded its healthier product lines, such as baked snacks and low-calorie beverages, tapping into the health-conscious market segment.
Strong Financial Position
With a reported revenue of approximately $91.4 billion in 2023, PepsiCo maintains a strong financial position. Consistent revenue growth and profitability enable the company to reinvest in product innovation, marketing, and sustainability projects. For instance, PepsiCo’s investment in plant-based snack options and zero-sugar beverages reflects its ability to fund long-term initiatives that align with consumer trends.
Financial stability also allows the company to undertake strategic acquisitions, such as the purchase of Rockstar Energy and Poppi, broadening its product offerings and expanding market share.
Global Distribution Network
PepsiCo’s extensive global distribution network is a vital strength. The company ensures that its products are widely available—from urban supermarkets in New York to rural kiosks in India. This reach is supported by robust logistics, partnerships, and local manufacturing facilities, allowing PepsiCo to adapt products to regional tastes and preferences.
The company’s ability to navigate complex global supply chains was especially tested during the COVID-19 pandemic, where disruptions were quickly managed to keep shelves stocked worldwide.
Strategic Acquisitions
PepsiCo’s growth strategy includes strategic acquisitions that enhance its market presence and product variety. Notable examples are the acquisitions of Rockstar Energy, boosting PepsiCo’s footprint in the lucrative energy drink segment, and Poppi, a brand focused on gut-health beverages with prebiotics.
These acquisitions align with the shifting consumer demand toward functional and health-oriented drinks, illustrating PepsiCo’s forward-looking approach to market trends.
Weaknesses
Health Perception
Despite its diversified portfolio, PepsiCo faces significant health perception challenges. Many of its products, especially carbonated beverages and some snacks, are criticized for high sugar, salt, and fat content. This negative perception has led to increased scrutiny from health advocates, governments, and consumers.
For example, in countries like the UK and Mexico, sugary drink taxes and advertising restrictions have affected sales and forced companies like PepsiCo to rethink product formulations and marketing strategies.
Dependence on Carbonated Beverages
A large portion of PepsiCo’s revenue still depends on carbonated soft drinks (CSDs), particularly Pepsi-Cola. However, global consumption trends show a steady decline in soda sales due to growing health awareness and lifestyle changes.
This overreliance exposes the company to risks if these declining trends accelerate, as seen in North America and parts of Europe, where soda consumption per capita has dropped significantly over the past decade.
Environmental Impact
PepsiCo faces growing concerns related to its environmental impact, especially around plastic waste and water usage. As a major producer of packaged beverages and snacks, the company contributes to plastic pollution challenges worldwide.
While PepsiCo has committed to sustainability goals, including reducing virgin plastic usage and improving water efficiency, critics argue that the scale of the problem remains substantial. Environmental groups have repeatedly called on PepsiCo to accelerate its eco-friendly initiatives and enhance transparency in reporting.
High Debt Levels
PepsiCo carries significant long-term debt, which may limit its financial flexibility and increase interest expenses. High debt levels can constrain investment capacity, especially during economic downturns or periods of rising interest rates.
In 2024, rising global inflation and interest hikes increased debt servicing costs for many large corporations, including PepsiCo, adding pressure on profitability margins.
Opportunities
Health-Conscious Products
With consumers increasingly prioritizing wellness, PepsiCo has vast opportunities in health-conscious product development. The rise of plant-based snacks, low-sugar beverages, and functional foods opens new markets.
PepsiCo’s recent launch of products like LIFEWTR and its commitment to reducing added sugars across portfolios exemplify this direction. The growing trend toward gut health and immunity also provides fertile ground for innovation.
E-Commerce Expansion
The surge in online shopping, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, offers PepsiCo new distribution channels through e-commerce platforms. Direct-to-consumer models and partnerships with online grocers enable the company to reach tech-savvy customers and improve data-driven marketing.
For instance, PepsiCo’s collaboration with Amazon and Walmart’s online portals allows for targeted promotions and subscription-based sales models, increasing consumer convenience and brand loyalty.
Sustainability Initiatives
Sustainability is no longer optional—it is a strategic imperative. PepsiCo’s investments in recycling technologies, sustainable packaging, and water conservation bolster its brand image and compliance with increasingly strict regulations.
In 2023, PepsiCo announced a significant reduction in plastic use by introducing biodegradable packaging in select markets. Such efforts not only address environmental concerns but also appeal to the growing segment of eco-conscious consumers.
Emerging Markets
Expanding presence in emerging markets like India, Africa, and Southeast Asia represents a major growth avenue. Rising incomes, urbanization, and changing lifestyles drive demand for convenient food and beverage products in these regions.
PepsiCo’s ability to tailor products to local tastes and price points has helped it gain ground in these markets. For example, the launch of region-specific flavors and affordable snack options has driven market penetration in India.
Threats
Intense Competition
PepsiCo faces intense competition from global giants such as Coca-Cola, Nestlé, and Unilever. These rivals continuously innovate and invest heavily in marketing, making it challenging to maintain market share.
For example, Coca-Cola’s aggressive push into the health and wellness segment with brands like Honest Tea and Costa Coffee has pressured PepsiCo to respond quickly and creatively.
Changing Consumer Preferences
Rapid shifts in consumer preferences toward healthier and natural products threaten PepsiCo’s traditional product lines. The growing popularity of fresh, organic, and minimally processed foods poses a challenge to mass-produced snacks and sodas.
Failure to adapt swiftly can result in lost market relevance and declining sales in developed markets where health trends are strongest.
Economic Factors
Global economic uncertainties, inflation, and potential downturns can reduce consumer spending power and affect PepsiCo’s profitability. Rising raw material costs and supply chain disruptions add to operational pressures.
In 2022-2023, inflationary pressures forced PepsiCo to increase product prices, risking consumer pushback and volume declines in price-sensitive markets.
Regulatory Challenges
Increasingly strict regulations around health standards, labeling, advertising, and environmental impact pose ongoing threats. Governments worldwide are imposing sugar taxes, banning certain additives, and requiring transparency on nutritional content.
PepsiCo must continuously adapt its compliance frameworks and product formulations to meet these evolving legal requirements, which can increase operational complexity and costs.
Strategic Recommendations
Product Reformulation
PepsiCo should prioritize developing and promoting healthier product alternatives, reducing sugar, salt, and artificial ingredients. Enhancing product transparency and nutritional value will build consumer trust and align with global health initiatives.
For example, reformulating classic products like Pepsi-Cola to offer low- or zero-sugar options, while expanding plant-based snack lines, will cater to the health-conscious consumer base.
Sustainability Focus
Intensifying efforts in recycling, biodegradable packaging, and water conservation will improve PepsiCo’s environmental footprint. Collaborating with governments and NGOs to create circular economy models can further enhance sustainability credentials.
Continued investment in sustainable agriculture practices will also secure long-term raw material supplies.
Market Diversification
Exploring new markets and demographics will mitigate risks from saturated or declining regions. PepsiCo can capitalize on emerging economies, younger consumers, and niche segments such as organic and functional foods.
Localized marketing campaigns and culturally relevant products will support successful market entry and growth.
Digital Transformation
Investing in technology to improve supply chain efficiency, data analytics, and customer engagement will enhance PepsiCo’s competitive edge. Embracing AI-driven demand forecasting and personalized marketing can optimize operations and boost sales.
Digital platforms also facilitate direct consumer relationships, enabling faster feedback loops and innovation cycles.
Competitors of PepsiCo
PepsiCo operates in a fiercely competitive industry, primarily the food and beverage sector, where several large multinational corporations vie for market share. Its main competitors are companies that challenge PepsiCo across various product categories—beverages, snacks, and nutrition. Below is a comprehensive analysis of PepsiCo’s key competitors:
The Coca-Cola Company
Coca-Cola is PepsiCo’s most direct and well-known rival, especially in the carbonated soft drinks segment. The rivalry between Pepsi and Coca-Cola is one of the most famous in business history, often called the “Cola Wars.”
- Coca-Cola’s flagship product, Coca-Cola soda, dominates many markets globally, especially in North America and Europe.
- Coca-Cola owns a vast beverage portfolio, including Sprite, Fanta, Minute Maid, and Dasani water.
- The company has been aggressively investing in healthier beverage options like Coca-Cola Zero Sugar and expanding into energy drinks with brands like Monster Energy.
Example:
In 2023, Coca-Cola launched a marketing campaign in the US called “Real Magic,” aimed at connecting emotionally with younger consumers, directly competing with PepsiCo’s branding efforts targeting the same demographic. This campaign helped Coca-Cola increase its market share in the US beverage sector by 2% in Q4 2023.
Nestlé S.A.
While Nestlé is primarily known as a food company, it is a strong competitor to PepsiCo in various product segments, especially bottled water, coffee, and snacks.
Competitive Edge:
- Nestlé owns Nescafé, KitKat, Perrier, and Pure Life water, making it a major player in both food and beverage categories.
- The company emphasizes health and nutrition, an area where PepsiCo is also investing heavily.
- Nestlé’s presence in emerging markets is strong, providing tough competition for PepsiCo’s expanding footprint.
Example:
Nestlé’s acquisition of Blue Bottle Coffee in 2017 and its rapid expansion of premium coffee products has challenged PepsiCo’s coffee segment, particularly with PepsiCo’s Starbucks ready-to-drink coffee products, which it launched in partnership with Starbucks.
Unilever
Unilever competes mainly in the snacks and nutrition segments of PepsiCo’s business. Though better known for its personal care products, Unilever owns a substantial food and beverage portfolio.
Key Brands:
- Ice cream brands like Magnum, Ben & Jerry’s, and Walls compete with PepsiCo’s snack-related frozen dessert products.
- Unilever’s growing range of health-focused foods and snacks competes with PepsiCo’s efforts in healthier product lines.
Example:
In 2022, Unilever acquired The Vegetarian Butcher, expanding its plant-based food options. This move directly competes with PepsiCo’s offering of healthier, plant-based snack alternatives, reflecting a growing consumer trend towards sustainability and health.
Kraft Heinz Company
Kraft Heinz is a major competitor in the packaged foods and snacks market. Although not as diverse in beverages as PepsiCo, Kraft Heinz competes heavily in snacks, sauces, and convenience foods.
Competitive Factors:
- Brands like Kraft, Heinz, Planters, and Capri Sun are household names.
- Kraft Heinz has a strong presence in North America and Europe, challenging PepsiCo in snack foods and complementary products.
Live Example:
In 2023, Kraft Heinz launched Planters’ Nut-rition Bars as a direct competitor to PepsiCo’s protein and nutrition bars, capturing a segment of the health-conscious snack market that PepsiCo is also targeting.
Mondelez International
Mondelez is a major global snack company, competing directly with PepsiCo’s Frito-Lay division.
Strengths:
- Mondelez owns popular brands like Oreo, Cadbury, Toblerone, and Ritz, focusing heavily on biscuits, chocolates, and snacks.
- The company has a strong foothold in emerging markets, similar to PepsiCo.
Example:
Mondelez’s Oreo brand continues to be a top-selling biscuit worldwide, often competing with PepsiCo’s Lay’s and Cheetos for shelf space and consumer attention in snack aisles globally.
Red Bull GmbH
Red Bull is the dominant player in the energy drink market, directly competing with PepsiCo’s energy brands like Rockstar Energy.
Competitive Highlights:
- Red Bull has a cult-like following and strong global brand recognition.
- It leads the energy drink market with innovative marketing such as extreme sports sponsorships.
Example:
Red Bull’s sponsorship of Formula 1 and extreme sports events continues to give it an edge in brand visibility, making it a formidable competitor to PepsiCo’s efforts to grow its Rockstar brand in the energy segment.
Conclusion
PepsiCo remains a formidable player in the global food and beverage sector, buoyed by strong brands, a diversified product lineup, and a vast distribution network. However, it faces challenges from health concerns, environmental pressures, and shifting consumer behaviors.
A well-executed SWOT analysis of PepsiCo reveals that capitalizing on its strengths while addressing weaknesses is crucial for seizing emerging opportunities and mitigating threats. By embracing innovation, sustainability, and digital transformation, PepsiCo is well-positioned to navigate the complex market landscape in 2026 and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the primary strength of PepsiCo?
A1: PepsiCo’s primary strength lies in its strong global brand recognition and diversified product portfolio, which includes beverages, snacks, and nutrition products trusted worldwide.
Q2: Why is PepsiCo’s dependence on carbonated beverages a weakness?
A2: The global decline in soda consumption due to health concerns makes PepsiCo’s reliance on carbonated drinks a vulnerability, risking revenue drops if trends continue.
Q3: How is PepsiCo addressing environmental challenges?
A3: PepsiCo is investing in sustainable packaging, water conservation, and recycling programs to reduce its environmental impact and meet regulatory standards.
Q4: What opportunities does PepsiCo have in emerging markets?
A4: Growing urbanization, rising incomes, and changing consumer lifestyles in emerging markets provide PepsiCo opportunities to expand product offerings and increase market share.
Q5: How does intense competition affect PepsiCo?
A5: Competitors like Coca-Cola and Nestlé continuously innovate and invest in marketing, which pressures PepsiCo to stay agile and invest in product and marketing innovation.

